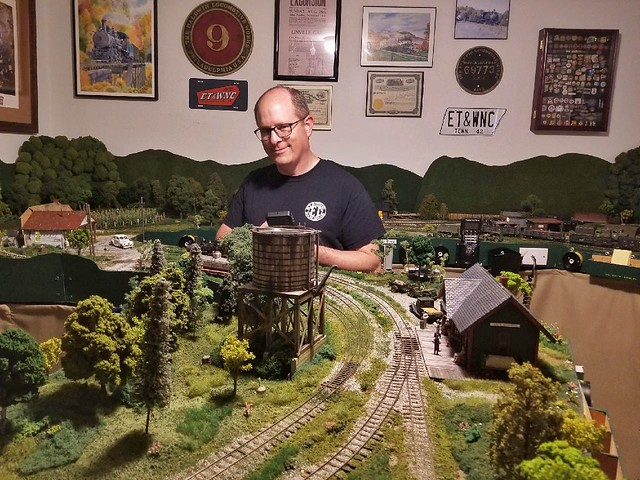
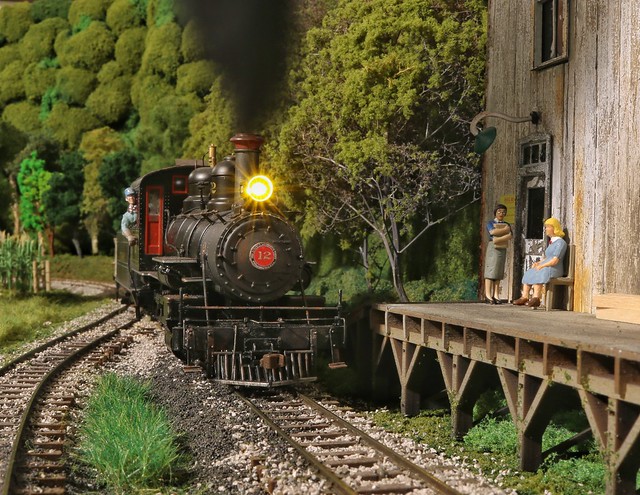
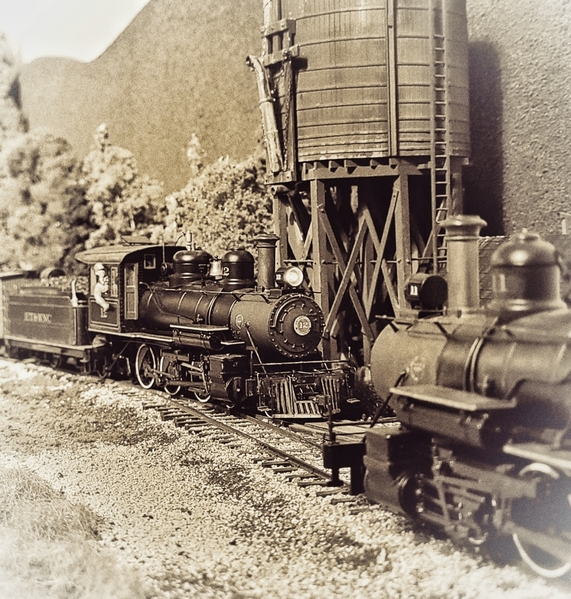
Awesome! This was an unexpected element of model railroading that I really enjoy. Making up the backstory has been a lot of fun for me and I'm glad you have a back story for your railroad.
I'm not sure I have it posted here already, but here's my complete fictional history of the Stoney Creek Southern/ET&WNC Stoney Creek branch and locations in a modern-day context. I wrote this before I built the layout as a firm guide on how I was going to handle everything:
The railroad was started in 1898 and by 1900, cut East by Northeast from Elizabethton, paralleling old state 91 on the south side of the Watauga River. It crossed the Watauga at the bend in the river just east of the modern Lynn Valley Road bridge. Paralleling the current highway 91, it ran up into the hills where logging traffic kept the railroad going into the depression era. The railroad got as far as Dry Branch where locomotives were turned around and log cars were loaded. Originally chartered as the Stoney Creek RR, the line added 'Southern' to the end of the name to avoid confusion with state tax collectors over a competing logging line which ran mostly on the south side of the creek. There were various station stops once the railroad crossed the Watauga River, notably at stops such as Hunter, Winner, Sadie and Buladeen. The line was chartered to go as far as Shady Valley, but never got that far.
From the bridge crossing and interchange to the end of the line, the railroad was just a little bit over 12 miles in length. Turntables were put in at each end of the line to turn around the 4-4-0s and logging engines seen on the line after a bad grade crossing accident when a locomotive was facing the opposite direction of travel.
The line saw very little passenger traffic but the logging provided revenue until the 1930s. By 1936, trains were running only once a day, if that. Drowning in red ink, the Stoney Creek Southern offered a buyout of stock to the parent company of the East Tennessee & Western North Carolina RR. By the fall of that year, SCS-marked rolling stock started to vanish and ET&WNC equipment started running up the valley. Although a separate corporate entity into the WW2 years, the SCS was in effect another branch of the 'Tweetsie'.
The third storm of the 1940 hurricane season (they weren't named at this time) caused much flooding in the region and washed out the SCS's Howe truss bridge across the Watauga. The ET&WNC filed for abandonment soon afterward, citing declining traffic and the cost of rebuilding the bridge. The ICC ruled against the ET&WNC once they reviewed the current condition of the rest of the line. The Watauga River bridge was the primary damage to the line, which saw surprisingly little damage from flooding along Stoney Creek as the line was built well above the level of the creek in most spots. Only a short section near the Speedwell was washed out and a review of revenues showed a lack of interest in running mixed trains as opposed to a lack of customers, most notably the logging loadout near the end of track and the large barrel component factory midway along the line. Several sections of rail were brought out of Boone when the Linville River Railway was abandoned. The ICC strongly pushed for use of the roadbed of the recently-abandoned Virginia and Southwestern RR (later owned by the Southern Railway) where it crossed the river. However, the railroad was rebuilt where it was. This remains the only known case of a standard-gauge railroad being abandoned in favor of a narrow-gauge common carrier in American history. ET&WNC crews would often point out the remaining abandoned SRR trackage and joke with traveling soldiers and newcomers to the valley that, "we even outlasted the big railroads!" Still, the line continued to struggle from lack of operational interest by parent ET&WNC.
Pearl Harbor changed all that.
By late 1941, the Army had already considered placing an infantry training camp somewhere in the Shady Valley area, but the lack of good roads prevented this. By the spring of 1943, the Army placed a Railway Operating Battalion into the valley with the specific mission to rebuild the aging SCS mainline (by now referred to the Stoney Creek branch of the ET&WNC). This was for the shared purpose of training Army forces in rebuilding damaged railroads for the future liberation of Axis-held nations and also to provide a good transportation hub into the valley for a projected training camp for the Army ground forces. New 55-pound rail was laid and new ballast brought in for the main line before the Summer of 1942.
ET&WNC locomotive # 14, originally designated to go to the White Pass and Yukon RR in Alaska along with # 10, was instead headed into the Valley near its home rails instead for Army use. Many soldier-railroaders who cut their teeth on the ET&WNCs ten-wheelers went on to run trains on the White Pass & Yukon in Alaska as well as meter-gauge rail lines in Africa, Europe and Asia.
The turntables were still being used but were no longer as useful as the shorter locomotives they were made for were no longer around. Turning a 4-6-0 on either of them was a balancing act with only an inch or two to spare on each end that none of the crews enjoyed doing. By the spring of 1943, the SCS had been rebuilt into a line the locals could be proud of. The tracks were still weed-covered in the summer months and the sidings weren't exactly to any Class I railroad standard, but the track was in better condition than it had ever been.
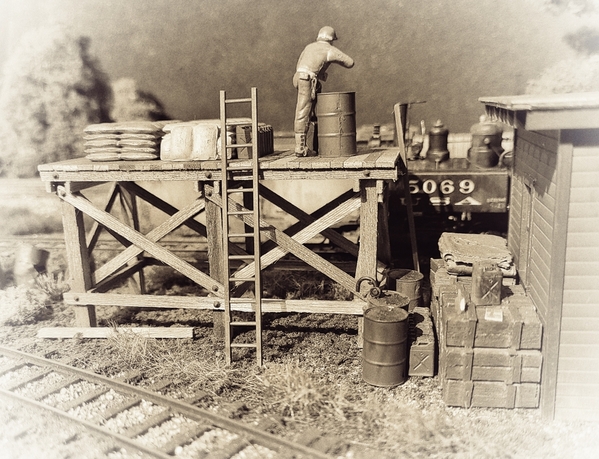
Commuter trains heading for the rayon mills in Elizabethton provided hundreds of skilled workers for needed defense work. Soldiers used the Stoney Creek branch to transport various loads of weapons, munitions, vehicles and supplies. The 3-foot line into the valley had never seen such traffic before, especially now that gas rationing had rendered civilian motor traffic all but useless without available gasoline.
It is now late summer in 1943. The line hauls mixed freight, cord wood, military traffic and passenger trains for the mills almost round-the-clock. The Army is also using the line for defense purposes. Soldiers are often seen coming in and out of the valley, further contributing to the local wartime economy.
This is the high-water-mark for the narrow gauge along Stoney Creek.